Complete Guide To Working At Height Regulations
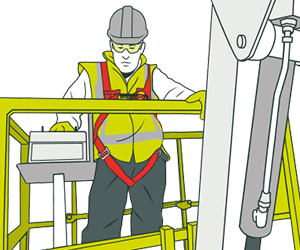
The Health and Safety Executive (HSE) defines work at height as any piece of work done at any such place where the absence of any precautions could make a person fall a distance liable to cause personal injury.
The Work at Height Regulations 2005 enlists a set of specific guidelines that aim to avert death and injury caused due to a fall from height. These guidelines have been setup specifically for the employers who either employ people to work at height or control the same.

Level 1: Avoid working at height whenever possible.
It is important for an individual to avoid working at height whenever feasible. This should be done to keep oneself safe as well as the employer from any complications. Meeting this requirement demands one to work as much as possible from the ground using extending tools. These tools can easily replace the use of a ladder, or the need to lower something to ground level before repairing it.
Level 2: Work in an existing safe place when possible.
To avoid falls, one must try and make use of an existing workplace. This should be done to prevent any falls and later deal with its consequences. One can execute the required work at such a place where there is no need of any additional protective equipment as well as there is no risk of falling since preventative measures are already in place. Common examples include a balcony or on machinery that has fixed guard rails.
Level 3: Prevent falls by using the collective equipment.
In case, a person is required to work at some other place and requires him/her to assemble or disassemble the framework, it is best to avoid falls by using the collective equipment. Making use of as external advance guardrails or collective protection units can be used to prevent falls and keep everyone safe.
Level 4: Use PPE to prevent falls.
The last way to prevent fall at a job is by using personal protective equipment (PPE). One of the common equipment is belts with short lanyards to restrict the worker’s movement. Making use of PPE helps prevent falls completely.
Level 5: Minimise distance using collective equipment.
Another way to prevent a fall is by reducing the distance between the person and the ground. It is important for a person on duty to make sure that the distance is minimized between him/her and the ground, which, in turn, helps reduce the risk of fall. Some of the easy ways to do so include placing netting or airbags beneath the work area, and close to it.
Level 6: Mitigate distance using PPE.
The purpose behind wearing a PPE is to make sure that in case a worker falls, the distance between their level and the ground level is minimal. For instance, if a worker is employed at a job location that involves a platform or framework, the distance is typically mitigated through the use of fall arrest harnesses. However, there is still a risk of causing serious injury and also, these are not much effective at lower heights.
Level 7: Minimise consequences using collective equipment.
One can minimize the fatal consequences of fall by using collective equipment such as netting or airbags. But, the purpose behind using this equipment this time is not to reduce the distance of fall but to soften the impact.
Level 8: Minimise consequences through proper training & instructions.
The best way to minimize the consequences of a risk is by imparting proper training and instructions to the workers who are working at height. This refers to educating workers about the best measures they can take to ensure their safety and prevent falls.
It is a combined responsibility of both employer and employee to ensure that each one of them stays safe and secure. None of the two can ensure the safety of all alone. After all, team work is the key.